2 Job Architecture Framework Examples to Try in 2026
What is Job Architecture?
Job Architecture framework is the structured design and organization of roles within a company. It defines how jobs are categorized, how they relate to one another, and the framework used to evaluate and manage them. This system includes job families, levels, titles, descriptions, and competencies. The goal is to ensure clarity, fairness, and consistency in talent management decisions, including hiring, compensation, and career progression.
As a foundational element in strategic workforce planning, a well-designed job architecture framework helps organizations scale effectively and remain agile in response to change. Rather than treating roles as static or siloed, modern businesses are shifting toward a dynamic job architecture approach that continuously evolves to reflect shifting skill demands, emerging technologies, and business priorities. Today, many companies are turning to AI-driven job architecture platforms and job architecture digitization tools to build resilient and scalable systems.
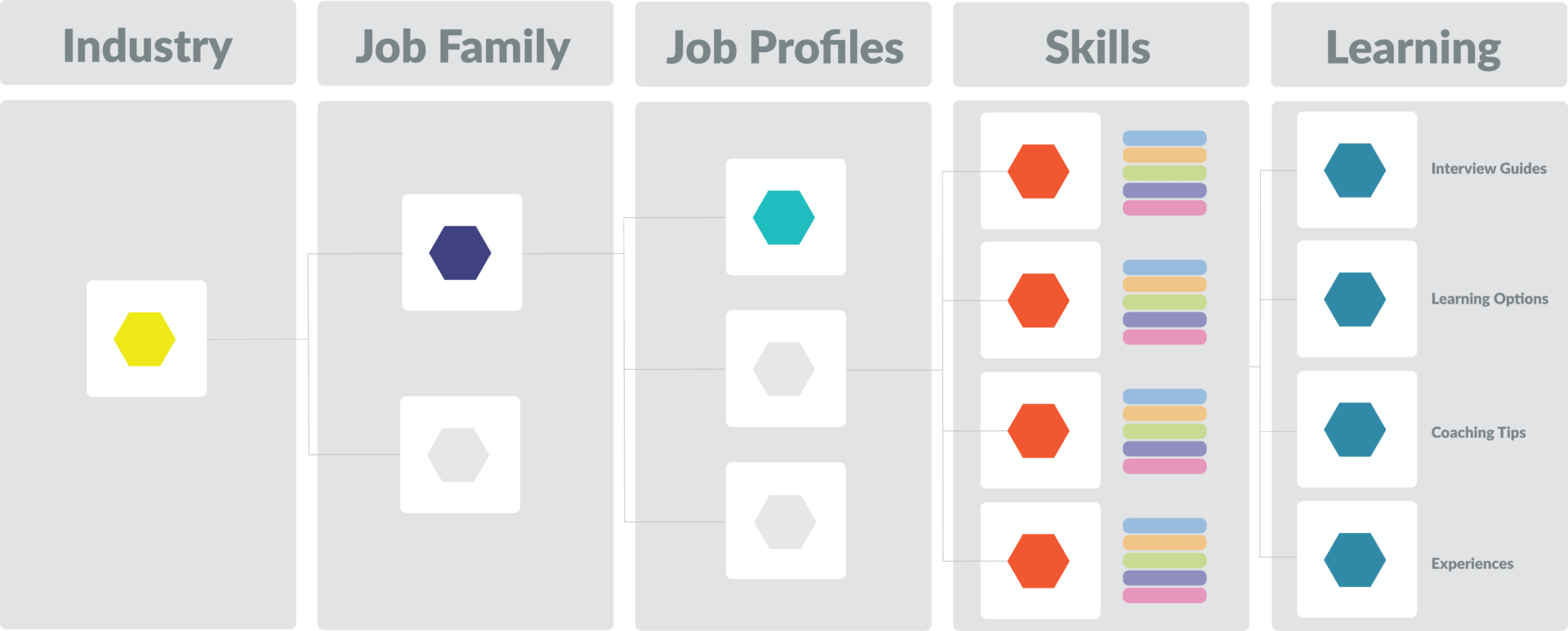
What are the Components of Job Architecture?
Job architecture consists of several critical components that help structure an organization’s workforce transparently and consistently. These include:
- Job Families: Broad groupings of roles that share common skills or functional responsibilities (e.g., Finance, Engineering, Marketing).
- Job Levels or Grades: Define the scope, responsibilities, and compensation for roles within each family through clear hierarchical tiers.
- Job Descriptions: Specify each role’s purpose, responsibilities, required qualifications, and core competencies.
- Competency Models: Identify the knowledge, skills, and behaviors employees need to perform successfully.
- Career Pathways: Map out structured paths that guide employees in their careers.
- Job Titles and Codes: Use standardized naming and classification systems to ensure clarity and organizational alignment.
Companies strengthen mobility, ensure pay fairness, and build skill-based strategies when they align these elements. When implemented with a robust job architecture tool or software solution, these elements contribute to an integrated system that promotes fairness and organizational efficiency. Additionally, job architecture consulting services often focus on refining or recalibrating these components for maximum alignment with business strategy.
Job Architecture Examples
Seeing job architecture in action helps illustrate how various industries apply frameworks to support operational goals and workforce planning. The best examples show how a company translates abstract structures into practical systems that drive business impact. Whether through job architecture software or a digitization tool, these examples reflect the real-world application of job architecture frameworks at scale.

Each example below demonstrates how a dynamic job architecture improves agility, employee engagement, and workforce intelligence. Tech and healthcare organizations use these frameworks to build a shared language and structure around roles and skills.
Example 1: Tech Company Job Architecture
A growing tech company with diverse engineering and product roles adopted a job architecture platform to organize its talent across multiple business units. They used a job architecture framework to organize roles into clear job families like Software Development, DevOps, Product Management, and User Experience, each with defined levels and career paths to promote mobility and upskilling.
The company dynamically mapped skills to roles using AI-driven job architecture tools, ensuring each job description reflected current technologies and market demands. With integrated analytics from a job architecture digitization tool, HR leaders gained insight into skill gaps and succession planning needs. Clear career progression empowered employees and strengthened both agility and retention.
Example 2: Healthcare Job Architecture
A regional healthcare network addressed inconsistencies in job descriptions and role expectations by partnering with a job architecture consulting firm and rebuilding its job structure using a standardized job architecture tool. The organization aligned nursing, medical support, and administrative job families under a unified grading system, using competency models tailored to patient care standards and regulatory requirements.
The new job architecture software allowed HR teams to maintain real-time updates to job descriptions and training pathways. Dynamic job architecture increased equity, cut hiring confusion, and clarified career paths. It helped the organization hit both care and talent goals.
The Benefits of Job Architecture
Implementing job architecture unlocks many benefits for organizations that manage their talent strategically. Employers enhance retention and engagement by helping employees see the path forward. They apply consistent standards to roles with job architecture, ensuring fair, data-driven pay while using dynamic structures to boost workforce agility.
Organizations can quickly respond to market changes and shifting skill needs by defining job roles through a flexible framework supported by real-time data. A strong job architecture platform ensures alignment between HR processes and business strategy, while job architecture digitization tools further streamline updates and analytics. HR leaders use these systems to make quicker, more accurate decisions about workforce planning, succession, and training investments.
Job Architecture Versus Organization Reporting Structure
Job architecture and reporting structure define workflows, though they focus on different goals. Job architecture defines roles by detailing responsibilities, required skills, and cross-functional connections. A reporting structure defines the hierarchy of authority, clarifies reporting relationships, and explains how teams receive supervision.
Confusing the two can lead to misaligned expectations and inefficiencies. For example, two employees may sit at the same level in the organizational chart but perform vastly different work requiring different skills. A solid job architecture framework allows more explicit comparisons and talent management decisions by evaluating roles based on function, not reporting lines. Organizations that adopt job architecture software can maintain consistency across both structures without overlap or redundancy.
By keeping job architecture and reporting structures distinct but aligned, businesses can promote role clarity, talent mobility, and cross-functional collaboration—essential for thriving in today’s fast-paced work environments.
How to Set Up Your Job Architecture
Setting up a job architecture begins with identifying the foundational elements of your workforce: the roles you currently have, the skills those roles require, and how they align with business goals. Start by grouping jobs into families and sub-families. These categories should reflect everyday responsibilities, competencies, or functional areas. After grouping roles into families, establish clear job levels such as entry-level, mid-level, senior, and leadership tiers.
Create detailed job descriptions that specify duties, qualifications, behavioral indicators, and competencies. Use a job architecture tool or software to automate labor market data collection, align skills with roles, and maintain consistency across departments. Document and manage your framework in a centralized platform or digitization tool to keep job data standardized, accessible, and current. HR, business units, and leadership stakeholders validate the framework and drive its adoption through active engagement. Many organizations also benefit from job architecture consulting support during this stage, especially when reworking outdated or siloed systems.
Once implemented, your job architecture becomes a living system. With dynamic job architecture capabilities, it can evolve as roles change and new skill requirements emerge. This positions your organization to stay agile, data-driven, and prepared for future workforce challenges.
Job Architecture with AI
Overcoming job architecture management barriers with artificial intelligence (AI). Traditional approaches to job architecture are costly and ineffective. AI-powered job architecture offers a more efficient, scalable, and dynamic solution.
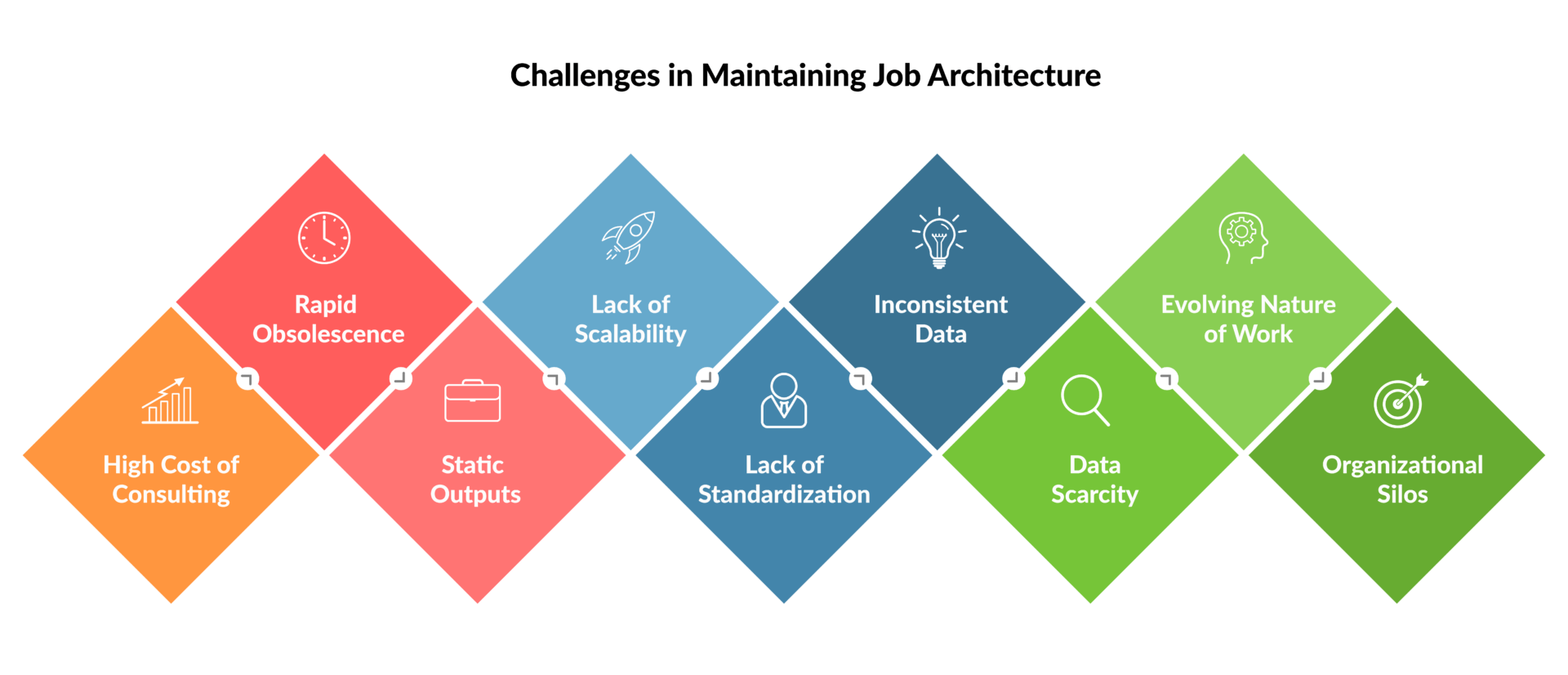
The Limitations of Traditional Job Architecture
Companies that rely on traditional job architecture methods—especially consultant-driven and manual processes—struggle to meet modern workforce demands. Although this approach plays a vital role in talent management, it has high costs and limited scalability.
Despite their knowledge, consultants often deliver job data that quickly becomes outdated and doesn’t support today’s digital talent management needs.
High Cost of Consulting
Consultants charge a premium for developing job descriptions, typically billing upwards of $1,000 per hour. With an average of 4 hours required to create a single skill-based job description, the cost per role can reach $4,000. For mid-sized companies with 20 to 50 roles in a job family, such as marketing or engineering, the total price can range from $80,000 to $200,000. The investment may initially appear worthwhile, but consultants deliver job descriptions as static PDF or Word documents.
Rapid Obsolescence
The fast-paced job market renders static job descriptions outdated almost immediately after creation. For organizations that rely on these static documents, the result is a mismatch between workforce capabilities and business needs. Companies risk falling behind in their talent strategies without the ability to adapt job data in real-time.
Static Outputs
Static PDFs and Word documents restrict job descriptions from supporting digital talent systems or offering live data on skills and competencies. As a result, organizations struggle to:
- Track and manage skills dynamically
- Update job descriptions to reflect changing roles
- Align jobs with evolving business strategies
Lack of Scalability
Organizations struggle to spot emerging skills and adjust to change when they rely on outdated, traditional methods.
Lack of Standardization
The lack of standardized practices for defining roles and skills leads to confusion, ambiguity, and challenges in comparing job roles or setting compensation.
Inconsistent Data
When teams use different job descriptions and skill criteria, they create confusion, hinder role alignment, and make it harder to spot skill gaps.
Data Scarcity
Data scarcity can hinder organizations from accurately defining roles and skills, as essential insights like performance metrics, skill assessments, or market trends may be inaccessible.
Evolving Nature of Work
The evolving nature of modern work—shaped by hybrid models, project-based tasks, and the gig economy—blurs the boundaries of traditional job roles, making them harder to define and manage.
Organizational Silos
Rigid departmental silos can fragment efforts, making it difficult to establish a cohesive and consistent job architecture across the organization.

The Need for a Modern Approach
Organizations use scalable, digital-first solutions to build and manage job architecture efficiently. AI-powered platforms like TalentGuard’s WorkforceGPT and Intelligent Role Studio replace outdated consulting methods and allow businesses to:
- Rapidly create and scale job architectures tailored to unique needs
- Continuously update job descriptions and skill data in real-time
- Integrate seamlessly with digital talent management practices
By leveraging AI, companies can reduce costs, maintain relevance, and ensure their job architecture evolves alongside business demands.
How TalentGuard Replaces Manual Services and Legacy Systems
By applying cutting-edge AI, TalentGuard gives organizations a more innovative way to manage job architecture—reducing complexity, saving time, and staying on strategy. Here’s how it changes the game:
- Data Analysis: TalentGuard’s AI processes large volumes of data to identify trends, inconsistencies, and skill gaps.
- Uniform Practices: AI builds consistent definitions for roles, skills, and behaviors across the organization.
- Predictive Insights: The system uses historical data and industry shifts to forecast skill demand.
- Dynamic Adaptability: AI updates job architecture in real time as role needs evolve.
- Personalized Recommendations: It delivers growth paths based on individual skills and career goals.
- Skill Gaps Identification: AI highlights specific training needs for precise upskilling.
- Career Path Generation: The system maps logical internal mobility pathways automatically.
- Workforce Optimization: AI aligns employee potential with strategic workforce needs.

TalentGuard: Job Architecture with AI WorkforceGPT
Today’s fast-paced business environment demands a strong, adaptable job architecture. Traditional methods fall short—wasting time and limiting impact. TalentGuard changes that with AI-powered tools that simplify, modernize, and optimize job architecture management.
To see job architecture management with AI, request a demo or request a free trial of WorkforceGPT.
FAQ’s
What is an example of a job architecture?
A tech company might use job architecture by grouping roles into families like Software Engineering, Product Management, and UX Design, with levels such as Associate, Mid-Level, Senior, and Lead. Each level includes defined responsibilities, required competencies, and career pathways. AI-powered platforms may enhance this framework by mapping real-life skills and aligning roles with market trends and business goals.
How do you define job architecture?
Organizations use job architecture to structure roles, group them into families, define advancement paths, and clarify responsibilities and competencies. A strong job architecture framework provides hiring, compensation, and career development consistency by aligning each role with strategic business needs. Tools like a job architecture platform or digitization tool can streamline and standardize this process.
What is the difference between job design and job architecture?
Job design focuses on the content and structure of a specific role—what tasks an employee performs, how they perform them, and what tools or methods they use. In contrast, job architecture refers to the broader organizational framework that groups and aligns all roles across the company. While job design operates at the individual level, job architecture works at the structural level to define job families, levels, and progression paths.
What is another name for job architecture?
Job architecture may also be called a job structure, role framework, or job leveling system. In talent management and HR circles, it’s often associated with terms like career framework or job hierarchy model, mainly when used to guide compensation, performance, and progression planning.
What are the 4 types of job design?
The four main types of job design include:
- Job Rotation: Moving employees between roles to increase variety and reduce boredom.
- Job Enlargement: Adding more tasks of a similar level to increase role breadth.
- Job Enrichment: Increasing role depth through more responsibility, autonomy, or opportunities for growth.
- Job Simplification: Breaking jobs into simpler tasks for clarity or efficiency.
See a preview of TalentGuard’s platform
What Is Job Architecture? A 2026 Guide + 2 Examples
In many organizations, job structures can become inconsistent and disorganized over time. Similar roles might have varying titles, levels, and compensation across departments. These discrepancies confuse employees, hinder workforce planning, and increase the risk of pay equity challenges. The solution lies in a well-structured (JA). This article delves into job architecture, why it matters, the […]
Job Architecture Competitive Analysis
Job Architecture Competitive Analysis: See how TalentGuard compares to other Job Architecture legacy tools and consultants. Before we dive in let’s take a look at the manual process used by most companies today. The Evolution of Job Architecture: From Manual Processes to AI-Driven Solutions Creating job architecture has historically been a time-intensive, manual process involving […]
Implementing Career Pathing Software for Employee Growth
Implementing career pathing software is a powerful step toward empowering employees and aligning their skills with your company’s strategic goals. Career pathing enables employees to visualize their growth potential within the organization, understand the skills they need to advance, and see the pathways available for both vertical and lateral movement. However, the process can be […]