Skills Taxonomy Software
The ready-to-use system of truth
Our platform provides a world-class Skills Taxonomy Software. Don’t let your skills and competency data remain unused inside a spreadsheet. Get the ability to create or extend your competency frameworks, customize job profiles, assign learning and development options, govern workflow and collaborate with other talent management applications.
Create
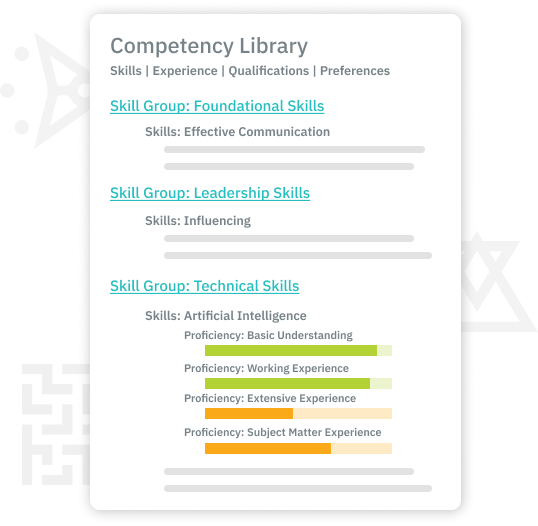
Ability to create, edit and compare multiple competencies, including: Skills, Experiences, Qualifications and Preferences that are required for job functions.

Map
Ability to map competencies, job grades, learning resources and other data to job profiles.

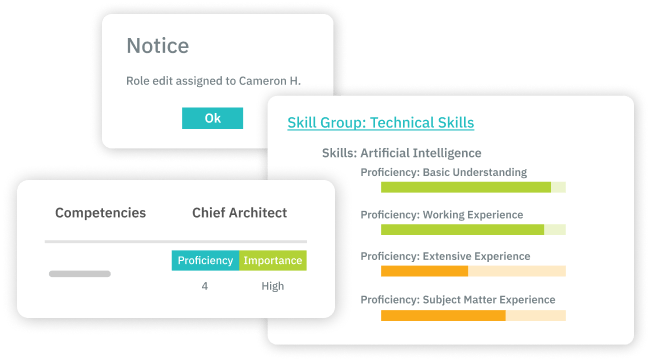
Calibrate
Job Profile calibration includes adjusting the level of proficiency and importance level of associated competencies across job profiles and grade levels.

Govern
Manage entitlement, rules, roles and policies to seamlessly govern job role data.
Choose Your Starting Point
All three options strengthen clarity across skills, readiness, and talent risk.
The difference is where you start—diagnosing trust, building the foundation, or seeing decisions in action.
Automate
Create skill profiles, create detailed job descriptions, align learning content with specific skills, and chart clear career path progressions to set the foundation for effective talent management.
Automate includes:
- Create Skill and Competency Profiles
- Develop Job Descriptions
- Map Learning to Skills and Competencies
- Map Career Path Progressions
Assess
Effectively assess their employees’ skills, identify gaps, and implement strategies to develop a skilled and competent workforce prepared to meet current and future challenges.
All the Automate features plus the ability to:
- Create a Skills Inventory
- Conduct Gap Analysis
Engage
Organizations can significantly enhance their talent development strategy and workforce effectiveness by assessing employee skills, curating personalized learning paths, recommending appropriate career paths, and tracking career goals.
All the Automate features plus the ability to:
- Assess Employee Skills and Competencies
- Curate Personalized Employee Learning Paths
- Recommend Employee Career Paths
- Track Career Goals
Optimize
Building talent pools, measuring employee performance, tracking certifications, and conducting multi-rater feedback enhance talent management, ensure compliance, and foster organizational leadership development.
All the Engage features plus the ability to:
- Build Talent Pools
- Measure Employee Performance
- Track Employee Certifications
- Conduct Multi-Rater Leadership Feedback
Trusted by Leading Companies Worldwide




Your Workforce is Evolving — Be Ready for What’s Next
Read our eBook
Additional information
If your organization wants to close skill gaps, create career paths for employees, and have a real-time record of the expertise present in your staff, skills taxonomy software is the key. First, let’s discuss what a skills taxonomy is and why it’s important for HR managers and business decision-makers.
A skills taxonomy is a list of all of the skills available in your workforce. It’s structured so that you can easily find which staff members have a needed skill, get a comprehensive picture of individual employees, or get a full picture of your entire workforce. With a skills matrix database, you can organize this information in a skills graph or reporting options to help you pinpoint the resources you have in house at any time.
With a larger number of employees and positions, it becomes even more important to develop a system to keep track of skills. Many of your employees have a diverse range of skills that are outside of the scope of work for their set position. Without a way to properly track the staff you have through a skills database, you’ll miss opportunities to close skill gaps and reskill and upskill staff.
A skills taxonomy dataset helps your hiring managers understand individual employees and where skill deficiencies are in staff to position the best candidates for future positions.
Skills Ontology vs Taxonomy
Skills ontology and taxonomy are different, but both useful in terms of understanding your organization’s skill data. First, let’s look at the definition of each.
A skill taxonomy database puts the information in a hierarchical classification system. From there, skills are placed into groups, called skill clusters, to better organize the information. This system allows employees to see which skills in the skills taxonomy they possess and how they relate to skills across the entire organization.
In a taxonomy database, the information is structured to position skills as they relate to positions and business strategy. And this placement of skills can be beneficial for employees because they can easily see which skills they need to master to propel their own career path. They can choose to learn new skills based on where they would like to move in their career.
A skills ontology dataset is a way to see different sets of skills in relation to one another. It can help aggregate large amounts of data in order to compare, simplify and maintain information and gain a new perspective on the skills in your database. Sometimes called a smart way to organize skill taxonomy, an ontology shows you relationships between the different skills databases. You can also use this to help you understand the relationship between different roles and how certain skills overlap and complement each other.
Skills Taxonomy Examples
A global skills taxonomy allows your organization to classify skills into groups and clusters to more productively pinpoint the talent needed at any given time. It also allows your hiring manager to plan forward by recognizing what new skills the team needs to learn or add with business objectives.
There are different kinds of skills taxonomies that you might use for your business. You might use a skills taxonomy that’s pertinent to your entire industry, or individual departments within your business. To highlight how this works in practice, let’s look at a few skills taxonomy examples.
Digital Skills Taxonomy
In today’s day and age, digital skills are important for nearly every type of job description. Of course, some departments will need more advanced skills than others. And there may be a crossover in digital skills because so much of the workforce use digital tools routinely.
Digital skills taxonomy structures might be categorized by the type of tool and then subcategorized by specific applications. For instance, your categories might include Communication Tools (such as email and workflow applications), Content Creation Tools (for your marketing and web content), Security (Cybersecurity and IT), Management and Problem Solving.
Information Technology Skills Taxonomy
An information technology skills taxonomy might be arranged by the needs of the IT department or company. For instance, some IT taxonomy would structure the information based on the Department and then on the application or IT use. Some would be structured based on the discipline of IT specialty, such as developer/coding, graphics/web design, data management, IT administration, IT security, Help Desk, and other specialties that might be represented in the organization.
Soft Skills Taxonomy
A soft skills taxonomy is just as integral as the hard skills hiring managers often prioritize. While it’s important to hire staff that are adept at the processes and workflows of your industry, it’s just as integral to hire based on personality, teamwork, and culture. Soft skills include skills such as teamwork, professionalism, and good communication.
How to Build a Skills Taxonomy
How do you build a skills taxonomy?
You can, technically, do this by hand or manually. You might be able to find an employee skills database template to guide you in the right direction and you can design your taxonomy in a way that seems structured best for hiring needs.
In a small company with few employees, this might be manageable through excel files or other tools that help organize a structure. Similar to the way you might plan your organizational chart. However, building a skills dataset by hand can be time-consuming and difficult. It can also be hard to update the information often enough to keep it relevant.
Using a software solution that gives you a skills inventory database and skills engine will streamline this process immensely. You will also find that the creation of your interactive skills taxonomy is much easier to complete. Intelligent software also allows for multiple views of reporting so that your team can maintain a good understanding of the workforce at any given time.
A software solution means that the skills of individual employees can be easily updated as they increase knowledge, add certifications, or gain experience through cross-training opportunities. You’ll also be able to easily pinpoint needs for upcoming hiring roles, so that job requirements include skills that will be necessary for the position and fill gaps within the organization.
Skills taxonomy solutions take the guesswork out of your hiring process and help your HR managers position employees to succeed and grow within your organization.
